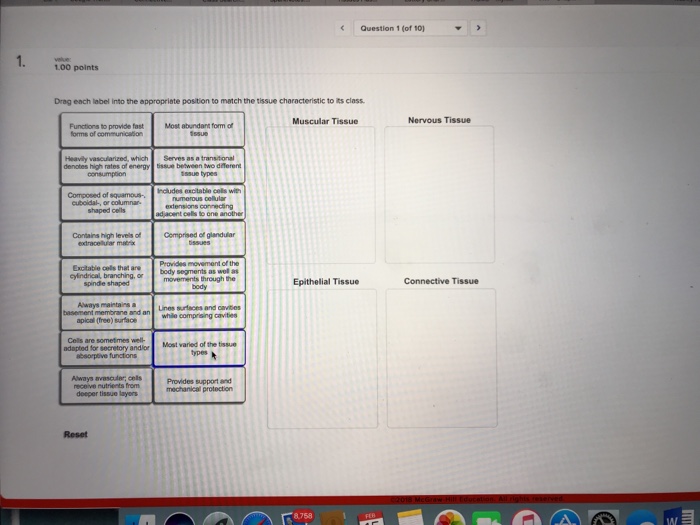
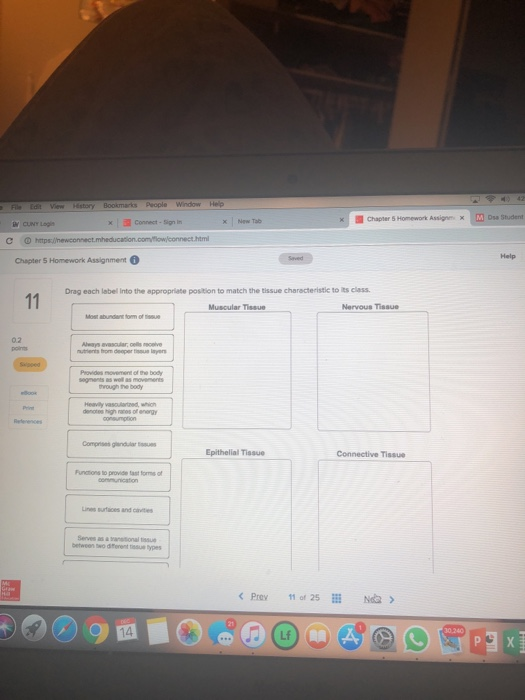
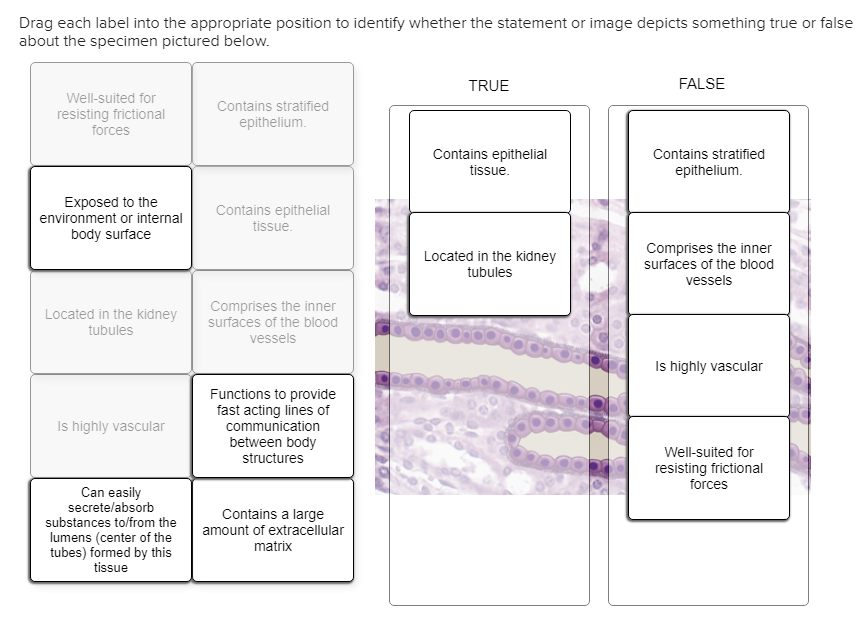
42 drag each label into the appropriate position to match the tissue characteristics to its class
Anatomical Position and Directional Terms | Anatomy and Physiology The anatomical position is a standing position, with the head facing forward and the arms to the side. The palms are facing forward with the fingers extended, and the thumbs are pointing away from the body. The feet are spaced slightly apart with the toes pointing forward. An easy way to remember this is to imagine that you're walking to the ... syn.mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk › acardona › fiji-tutorialFiji Programming Tutorial - University of Cambridge Load a color image stack and extract its green channel. First we load the stack from the web--it's the "Fly Brain" sample image. Then we iterate its slices. Each slice is a ColorProcessor: wraps an integer array. Each integer is represented by 4 bytes, and the lower 3 bytes represent, respectively, the intensity values for red, green and blue.
PDF In this chapter, you will learn that - Pearson We can describe smooth muscle tissue as visceral, nonstri-ated, and involuntary. Characteristics of Muscle Tissue What enables muscle tissue to perform its duties? Four special characteristics are key. Excitability, also termed responsiveness, is the ability of a cell to receive and respond to a stimulus by changing its membrane potential.

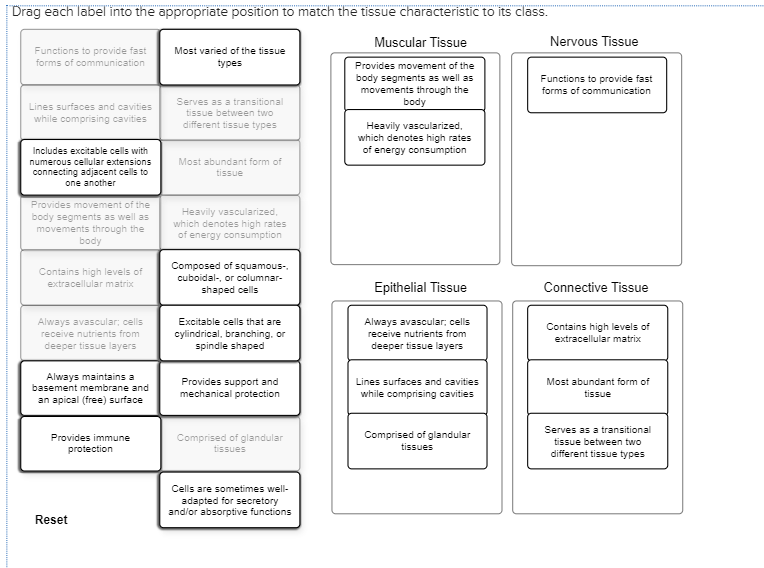
Drag each label into the appropriate position to match the tissue characteristics to its class
A Quick Comparison of Osteoblast Vs. Osteoclast Vs. Osteocyte Osteoblasts are formed from stem cells known as mesenchymal cells. These stem cells can also form cartilage tissues, as well as numerous other types of tissue. Osteoblasts are one of the end products of mesenchymal stem cells. They release collagen and some bone-forming proteins. This is part of the bone matrix, known as organic matrix. A&P Chapter 11 Nervous System 2 Homework - GraduateWay Drag and drop each label into the appropriate box, identifying which division of the autonomic nervous system is responsible for the given function. Label the general pattern of neurons and neurotransmitters associated with the autonomic nervous system. The medulla oblongata is continuous caudally with the Spinal cord quizlet.com › 528697863 › anatomy-lecture-exam-1anatomy lecture exam 1 Flashcards | Quizlet Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like A positive feedback loop causes a self-amplifying cycle in which a physiological change leads to even greater change in the same direction., A negative feedback loop is a process in which the body senses a change and activates mechanisms to reverse that change., What ovarian hormone is involved in a positive feedback loop with ...
Drag each label into the appropriate position to match the tissue characteristics to its class. Cell Organelles - Types, Structure and their Functions - BYJUS Chloroplasts - Chloroplasts are double membrane-bound organelles, which usually vary in their shape - from a disc shape to spherical, discoid, oval and ribbon. They are present in mesophyll cells of leaves, which store chloroplasts and other carotenoid pigments. These pigments are responsible for trapping light energy for photosynthesis. successessays.comSuccess Essays - Assisting students with assignments online Get 24⁄7 customer support help when you place a homework help service order with us. We will guide you on how to place your essay help, proofreading and editing your draft – fixing the grammar, spelling, or formatting of your paper easily and cheaply. Energy Pyramid: Definition, Levels and Examples | Earth Eclipse An energy pyramid is useful in quantifying the transfer of energy from one organism to another along a food chain. Energy is higher at the bottom of the pyramid, but it decreases as you move up through the trophic levels. Namely, as energy flows through the various trophic levels, some energy is normally dissipated as heat at each level. Solved drag each label into the appropriate position to - Chegg See Answer drag each label into the appropriate position to match the tissue characteristic to its class Show transcribed image text Expert Answer 88% (17 ratings) Muscular tissue: 1. Provides movement of the body segments as well as movement through body. 2. Serves as a transitional tissue between two different tissue type. 3.
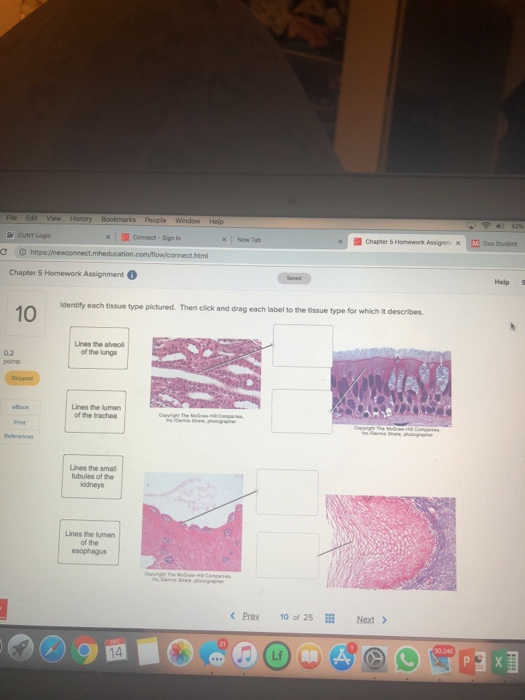
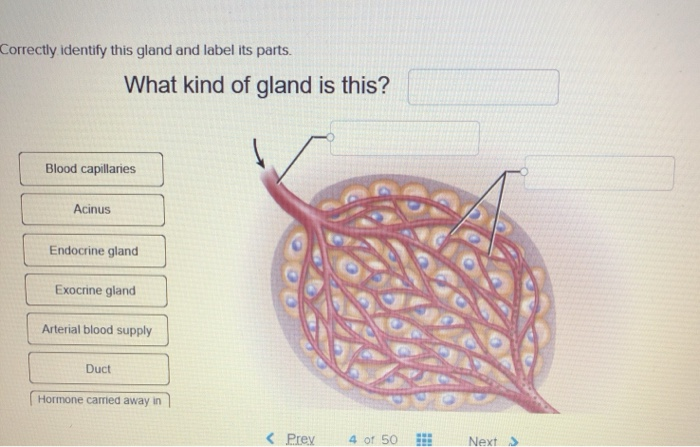
The Anatomical Regions of the Body - dummies The anatomical regions (shown) compartmentalize the human body. Just like on a map, a region refers to a certain area. The body is divided into two major portions: axial and appendicular. The axial body runs right down the center (axis) and consists of everything except the limbs, meaning the head, neck, thorax (chest and back), abdomen, and pelvis. The appendicular body consists of appendages ... Connect Homework Ch. 5 Flashcards | Quizlet Determine which connective tissue type each image below represents. Then click and drag the labels matching them up with the correct tissue type. Match each epithelial tissue type with its appropriate location in the body. Consider the two different ways that tissues can change. Then click and drag each scenario into the correct category. 4 Types of Tissues in Human Body and its Functions - Study Read The tissue consists of cells like fibroblasts, fat cells, macrophages, leukocytes, plasma cells, and mast cells. Their main role in the body is to. Protect. Transport and. Give Binding support. These are of many types like adipose tissues, reticular tissue, etc. This connective tissue is of different types as. quizlet.com › 578134211 › quiz-3-study-guide-flash-cardsQuiz #3 Study Guide Flashcards | Quizlet Drag each label into the appropriate position to match the tissue characteristic to its class. muscular tissue heavily vascularized which denoted high rates of energy consumption, excitable cells that are cylindrical branching or spindle shaped, provides movement of the body segments as well as movements through the body nervous tissue
AHCD1010HWSOL4.pdf - 4. Award: 1.00 point Problems? Adjust... Drag each label into the appropriate position to match the tissue characteristic to its class. Explanation: Even though trillions of cells can be found in the human body, they belong to approximately 200 cell types, which can further be organized into tissue types based on location, shape, origin, and function. › newsNews: Breaking stories & updates - The Telegraph Latest breaking news, including politics, crime and celebrity. Find stories, updates and expert opinion. Chapter 3 Cells And Tissues Worksheet Answers (2022) - s1.html Insulin is made by cells in the pancreas called beta cells that are arranged into clusters together with other pancreas cells. These clusters are called islets of Langerhans. 2. The UE performs the cell search procedure that is specific to the standard being used. This is done in order to get frame synchronization and cell ID information. 3. › 13079564 › cookery_g10_learningcookery g10 learning module - Academia.edu Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
Label the heart — Science Learning Hub In this interactive, you can label parts of the human heart. Drag and drop the text labels onto the boxes next to the diagram. Selecting or hovering over a box will highlight each area in the diagram. pulmonary vein semilunar valve right ventricle right atrium vena cava left atrium pulmonary artery aorta left ventricle Download Exercise Tweet
10 Levels of Biological Organization - Bio Explorer Levels of Biological Organization. #1. Cell. The cell is known to be the basic building block of life. It performs various metabolic functions like providing structure and rigidity to the body, converting food into nutrients and energy, and others.
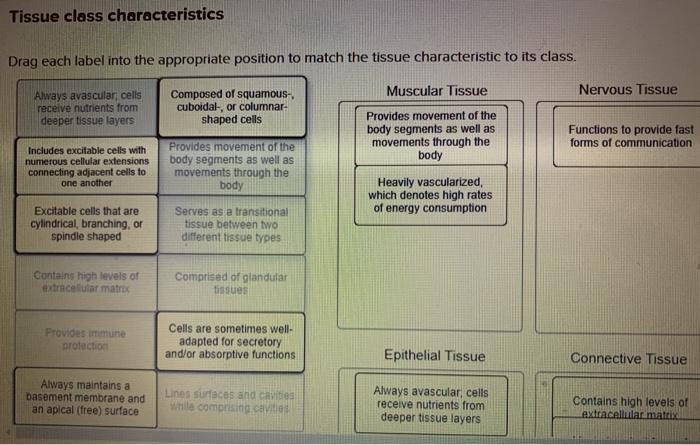
Solved Tissue class characteristics Drag each label into the - Chegg Tissue class characteristics Drag each label into the appropriate position to match the tissue characteristic to its class. Muscular Tissue Nervous Tissue Always avascular, cells receive nutrients from deeper tissue layers Composed of squamous- cuboidal-, columnar- shaped cells Provides movement of the body segments as well as movements through the body
Anatomy and Physiology: Anatomical Position and Directional Terms Up, Down, Side-to-Side: Directional Terms. Imagine that when you're studying a (correctly anatomically positioned) body you're looking at a map. Like you use the cardinal directions to explain the location of certain regions (north, northwest, southeast, etc.), you use directional terms to describe the regions of the body.
[Expert Answer] Drag the tiles to the boxes to form correct pairs ... State of matter is defined as a form in which matter can exist. There are four states of matter known till date. They are as follows: Solid: Matter is said to be in solid state if it has definite shape and volume. The components of matter are closely packed and have fixed positions within the matter.
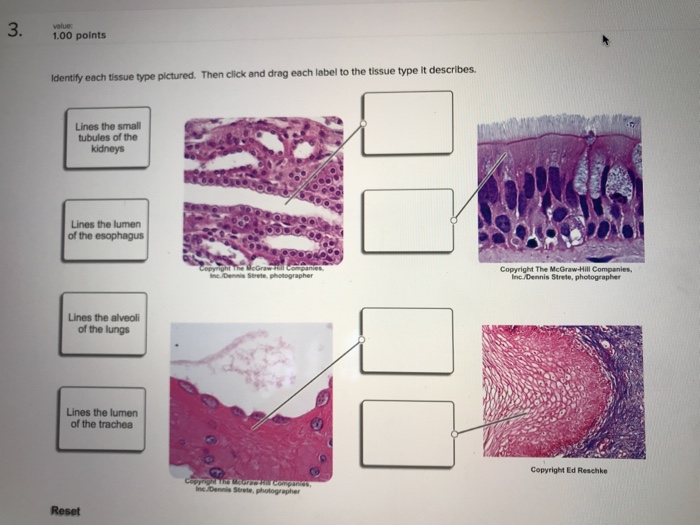
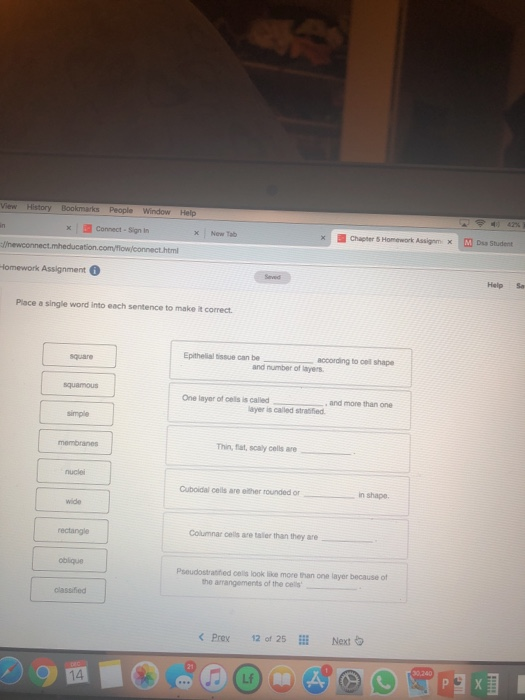
Types of Tissues - Anatomy & Physiology - University of Hawaiʻi The two broad categories of tissue membranes in the body are (1) connective tissue membranes, which include synovial membranes, and (2) epithelial membranes, which include mucous membranes, serous membranes, and the cutaneous membrane, in other words, the skin. Connective Tissue Membranes
Study Guide Of Tissue And Membranes ? - s1.html label the following areas on a slide of skeletal muscle., Drag each label into the appropriate position to match the tissue characteristic to its class., Place the characteristics with. Mark Klimek Blue book (ALL) NCLEX Study Guide - Quizlet most potent of antiviral meds, inhibit cell protein synthesis that interferes
Answered: Drag each of the labels to the… | bartleby Transcribed Image Text: Drag each of the labels to the appropriate position in order to identify whether this digestive tract example is likely to include the indicated tissue type. Dense regular connective tissue Stratified squarmos epithelium Fibrocartilage Cardiac muscle Esophagus Nervous tissue Reticular connective tissue Pseudostratified epithelium Transitional Blood Stratified cuboidal Smooth muscle epithelium Skeletal tissue Simple columnar epithelium Areolar connective Hyaline ...
Cell Organelles and their Functions - Rs' Science A cell organelle is a tiny cellular structure that performs specific functions within a cell. You can think of cell organelles as a cell's internal organs. For example, the nucleus is the cell's brain, and the mitochondria are the cell's hearts. Cell organelles are often enclosed by their own membranes, which divide the cell into many ...
assignmentessays.comAssignment Essays - Best Custom Writing Services Get 24⁄7 customer support help when you place a homework help service order with us. We will guide you on how to place your essay help, proofreading and editing your draft – fixing the grammar, spelling, or formatting of your paper easily and cheaply.
A Labelled Diagram Of Neuron with Detailed Explanations - BYJUS Axon- Axon is a tube-like structure that functions by carrying an electrical impulse from the cell body to the axon terminals for passing the impulse to another neuron. Synapse- This structure functions by permitting the entry of a neuron to move an electrical or chemical signal from one neuron to another neuron.
Cell Membrane Transport | 6 Types with Examples - Study Read The cell membrane is a delicate organ of the cell which regulates the movement of substances into and outside the cell. The cell membrane transport occurs in two major ways like 1. Passive transport Passive diffusion Facilitated diffusion Osmosis. 2. Active transport. Sodium potassium pump Bulk transport (phagocytosis and pinocytosis)
Skin Layers: Structure, Function, Anatomy, and More - Verywell Health Subcutaneous tissue is the innermost layer of the skin. It's mostly made up of: 4 Fat Connective tissues Larger blood vessels Nerves The majority of your body fat is stored in the subcutaneous layer. It insulates you against changing temperatures and protects your muscles and internal organs from impacts and falls. The subcutaneous layer also:
Drag each label to the correct location on the chart. Sort the ... Drag each label to the correct location on the chart. Sort the characteristics based on whether they describe volcanoes, earthquakes, or both. Earthquake-Volcano-Both-a. measured on the Richter scale b. lava comes out c. natural hazard d. caused by subduction d. forms a mountain e. occurs underwater f. measured using a seismograph
Classification of Joints - TeachMeAnatomy In this article, we shall look at the classification of joints in the human body. Classification by type of tissue: Classification by degree of movement: Fibrous - bones connected by fibrous tissue. Cartilaginous - bones connected by cartilage. Synovial - articulating surfaces enclosed within fluid-filled joint capsule. Synarthrosis ...
Drag Each Label Into The Appropriate Position To Match The Tissue ... Drag Each Label Into The Appropriate Position To Match The Tissue Characteristic To Its Class. Muscular Tissue Nervous Tissue Excitable Cells That Are Cylindrical, Branching, Or Spindle Shaped Made Up Of Glandular Tissues Excitable Cells That Are Cylindrical, Branching, Or Spindle Shaped Includes Excitable Cols With Numerous Cellular Extensions Connecting
2-1 Mastering A&P Lab Module Two Homework - StuDocu Match the appropriate layer of skin to its description. Hint 1. Consider tissue type characteristics. Think about the tissue types covered in Chapter 3. Key characteristics can help properly identify the layers of skin. Epithelium always has one free surface. Connective tissues are numerous and varied, but they all connect things in the body. Hint 2.
quizlet.com › 528697863 › anatomy-lecture-exam-1anatomy lecture exam 1 Flashcards | Quizlet Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like A positive feedback loop causes a self-amplifying cycle in which a physiological change leads to even greater change in the same direction., A negative feedback loop is a process in which the body senses a change and activates mechanisms to reverse that change., What ovarian hormone is involved in a positive feedback loop with ...
A&P Chapter 11 Nervous System 2 Homework - GraduateWay Drag and drop each label into the appropriate box, identifying which division of the autonomic nervous system is responsible for the given function. Label the general pattern of neurons and neurotransmitters associated with the autonomic nervous system. The medulla oblongata is continuous caudally with the Spinal cord
A Quick Comparison of Osteoblast Vs. Osteoclast Vs. Osteocyte Osteoblasts are formed from stem cells known as mesenchymal cells. These stem cells can also form cartilage tissues, as well as numerous other types of tissue. Osteoblasts are one of the end products of mesenchymal stem cells. They release collagen and some bone-forming proteins. This is part of the bone matrix, known as organic matrix.



























Komentar
Posting Komentar